Heart valve diseases can significantly impact the heart’s functionality and overall well-being. Fortunately, medical advancements have paved the way for effective treatments, including heart valve repair and heart valve replacement surgery. These procedures aim to restore normal blood flow, alleviate symptoms, and enhance patients’ quality of life. This article will delve into the details of heart valve repair and replacement surgeries, their indications, techniques, recovery, and outlook.
Understanding Heart Valve Diseases
Heart valves are essential for maintaining the unidirectional flow of blood within the heart. There are four valves in the heart: the aortic valve, tricuspid valve, mitral valve, and pulmonary valve. Over time, these valves can develop structural issues such as stenosis (narrowing) or regurgitation (leakage), leading to compromised blood flow and requiring valve replacement open heart surgery.
Common Causes of Heart Valve Diseases
The common causes of heart valve disorders that require heart valve replacement surgery include:
- Age-Related Degeneration: As people age, their heart valves may become thickened and less flexible, impeding their proper function.
- Congenital Defects: Some individuals are born with abnormal heart valves that require valve replacement and open heart surgery.
- Infections: Bacterial infections can damage heart valves, leading to dysfunction.
- Rheumatic Fever: Untreated streptococcal infections can cause inflammation of the heart valves, leading to scarring and deformities.
- Endocarditis: An infection of the inner lining of the heart can also damage heart valves.
Indications of Heart Valve Disease
Heart valve replacement surgery is considered when the valve’s dysfunction severely affects the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently or causes debilitating symptoms. Common indications include:
- Severe Symptomatic Stenosis: When the valve opening becomes significantly narrowed, limiting blood flow and causing symptoms like fatigue, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
- Severe Regurgitation: When blood leaks back through the valve due to improper closure, resulting in heart enlargement and reduced efficiency.
- Heart Failure: Valvular diseases that contribute to heart failure may require surgical intervention to improve the heart’s function.
- Recurrent Infections: If the valve is damaged due to repeated infections, surgery might be necessary.
Heart Valve Repair
Heart valve repair aims to restore the valve’s normal function while preserving its native tissue. This approach is preferred when feasible, as it maintains the natural structure of the heart. Some techniques for valve replacement open heart surgery include:
- Valvuloplasty: Repairing the valve by reshaping, resizing, or separating valve flaps to improve closure and prevent leakage.
- Annuloplasty: Repairing the valve’s annulus (the ring-like structure) to ensure proper valve closure.
- Commissurotomy: Opening fused valve flaps to improve blood flow in stenotic valves.
Heart Valve Replacement
In cases where repair is impossible, heart valve replacement surgery becomes necessary. This involves removing the damaged valve and replacing it with a prosthetic valve. The two major types of prosthetic valves are:
- Mechanical Valves: These are made of durable materials and are long-lasting, but patients need to take blood-thinning medications for the rest of their lives to prevent clotting.
- Biological Valves: Also known as tissue valves, these are usually made from animal tissue (bovine or porcine) or obtained from human donors. They do not require long-term blood-thinning medications after heart valve replacement surgery but may have a shorter lifespan.
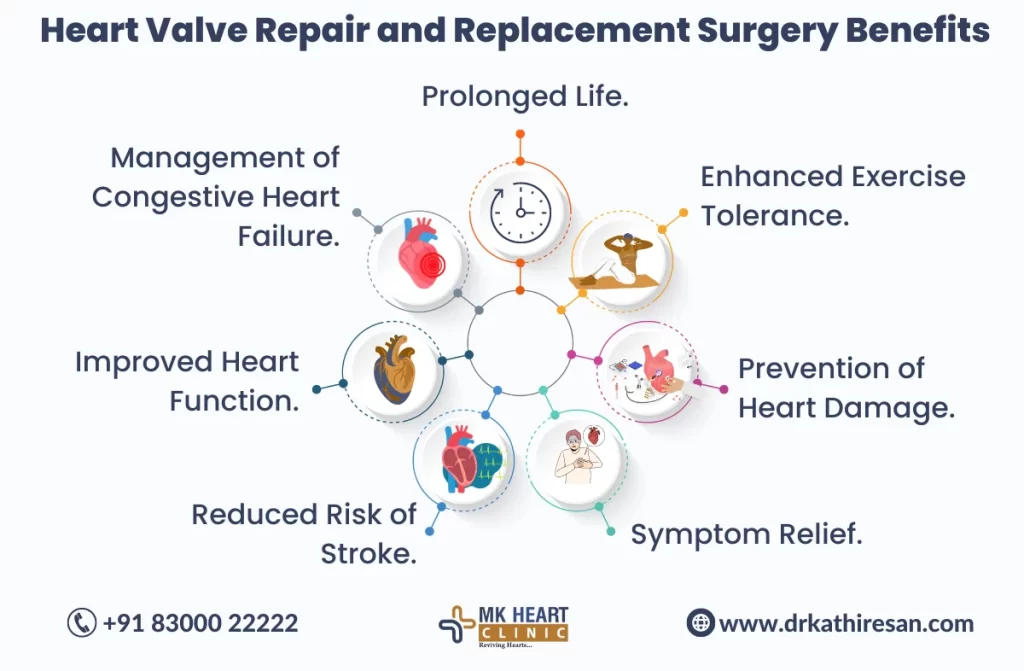
Heart Valve Replacement Surgery: Balancing Benefits and Risks
Heart Valve Replacement Surgery is a critical medical intervention designed to address valve-related heart conditions. Here are key points regarding the benefits and risks of this procedure:
- Improved Blood Flow: Heart Valve Replacement Surgery enhances blood flow by replacing damaged or malfunctioning heart valves, restoring optimal cardiac function.
- Symptom Alleviation: The surgery alleviates symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue, contributing to an improved quality of life.
- Prolonged Life Expectancy: Successful surgery can extend life expectancy, especially in cases of severe valve diseases that may lead to life-threatening complications.
- Enhanced Cardiac Performance: A properly functioning artificial valve contributes to improved cardiac performance, reducing the workload on the heart.
- Risks Associated: Despite benefits, risks include bleeding, infection, blood clots, and potential prosthetic valve-related issues.
- Types of Replacement Valves: Mechanical and biological valves are options, each with its own set of benefits and considerations.
- Individualized Approach: Decision-making considers the patient’s age, overall health, and lifestyle, ensuring an individualized treatment plan.
- Post-Surgery Care: Diligent post-surgery care is crucial, involving medication, lifestyle adjustments, and regular medical follow-ups.
Heart Valve Replacement Surgery remains a pivotal solution for those with significant valve issues, offering a chance for improved cardiac function and enhanced quality of life. Understanding the procedure’s benefits and risks is essential for informed decision-making regarding Heart Valve Replacement Surgery.
Surgery Procedure and Recovery
Heart valve replacement surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia and involves accessing the heart through an incision in the chest. Minimally invasive approaches are becoming more common, using smaller incisions and specialized tools for faster recovery.
Recovery after surgery involves a hospital stay, often requiring a few days in the intensive care unit and several more days in a regular ward. Patients are gradually encouraged to increase their physical activity, and cardiac rehabilitation may be recommended to aid in recovery.
Outlook and Lifestyle Changes
Following heart valve replacement surgery, patients often experience a significant improvement in their quality of life. Symptoms like shortness of breath and fatigue are alleviated, allowing for a more active lifestyle. However, patients will need to follow their doctor’s recommendations, which may include medications, regular check-ups, and lifestyle changes such as a heart-healthy diet and exercise.
Conclusion
To conclude, heart valve repair and replacement surgeries have revolutionized the treatment of heart valve diseases. These procedures offer hope for patients suffering from valve dysfunction, allowing them to regain their health and vitality. With ongoing advancements in medical technology, the outlook for those undergoing heart valve replacement surgery continues to improve, offering a brighter future for individuals dealing with these conditions.