A Chronic Total Occlusion (CTO) refers to a complete blockage that persists for three or more months in one of the coronary arteries, which are responsible for carrying blood to the heart. CTOs restrict blood flow to the heart, potentially leading to symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or even a heart attack. Chronic Total Occlusions in Chennai are observed mostly in individuals who are prone to coronary artery disease, with up to one in three people with CAD also having a CTO.
Several risk factors associated with CAD, such as smoking, obesity (BMI of 30 or higher), diabetes, family history of heart disease, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, a history of heart attacks or bypass surgery, and a sedentary lifestyle, increase the likelihood of developing a CTO.
Symptoms of Chronic Total Occlusions
Symptoms associated with Chronic Total Occlusions in Chennai may include chest pain, tightness or pressure, dizziness, fatigue, irregular heartbeat, nausea, racing or rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and upper arm pain. These symptoms often worsen during physical exertion and improve with rest. However, some individuals may experience symptoms at rest, while others may not display any symptoms at all.
Causes of Chronic Total Occlusions
CTOs primarily develop due to the accumulation of plaque, a fatty substance, in one or more coronary arteries. This plaque buildup, known as atherosclerosis, leads to the narrowing and hardening of the arteries, resulting in coronary artery disease. Several factors contribute to CTO development, including:
- Atherosclerosis – The buildup of plaque (cholesterol, fat, and calcium) in the arteries, leading to blockages.
- High Blood Pressure – Increases strain on arteries, accelerating plaque formation.
- Diabetes – Affects blood vessels, increasing the risk of arterial blockages.
- Smoking – Damages artery walls and promotes plaque buildup.
- High Cholesterol – Excess LDL cholesterol can contribute to narrowing and blockage.
- Sedentary Lifestyle – Lack of exercise leads to poor circulation and increased plaque deposits.
- Obesity – Increases the risk of heart disease and artery blockages.
- Genetics – Family history of heart disease can predispose individuals to CTO.
Managing risk factors through lifestyle changes and medical intervention can help prevent CTO and improve heart health.
Diagnosis and Tests
Healthcare providers typically diagnose a CTO through a coronary angiogram. This CTO intervention procedure involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels, which allows visualization of the coronary arteries on an X-ray and assessment of blood flow.
Additional tests that may aid in diagnosis include a CTO cardiac intervention to evaluate heart anatomy and blood flow, a cardiac stress test to observe the heart’s response to exercise, an echocardiogram to assess heart walls and valves, and an electrocardiogram (EKG) to examine the heart’s electrical signals and rhythm.
Management and Treatment of Chronic Total Occlusions In Chennai
The treatment approach for Chronic Total Occlusions in Chennai focuses on reducing symptoms and minimizing the risk of heart-related events, such as a heart attack. The specific treatment plan depends on the severity of symptoms and whether the individual is already undergoing treatment for coronary artery disease. Common treatment options include:
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): This CTO intervention procedure entails the insertion of a catheter through a blood vessel in the groin or wrist. The catheter is guided to the blocked coronary artery, where a small balloon is inflated to clear the plaque and a stent is placed to keep the artery open and restore blood flow.
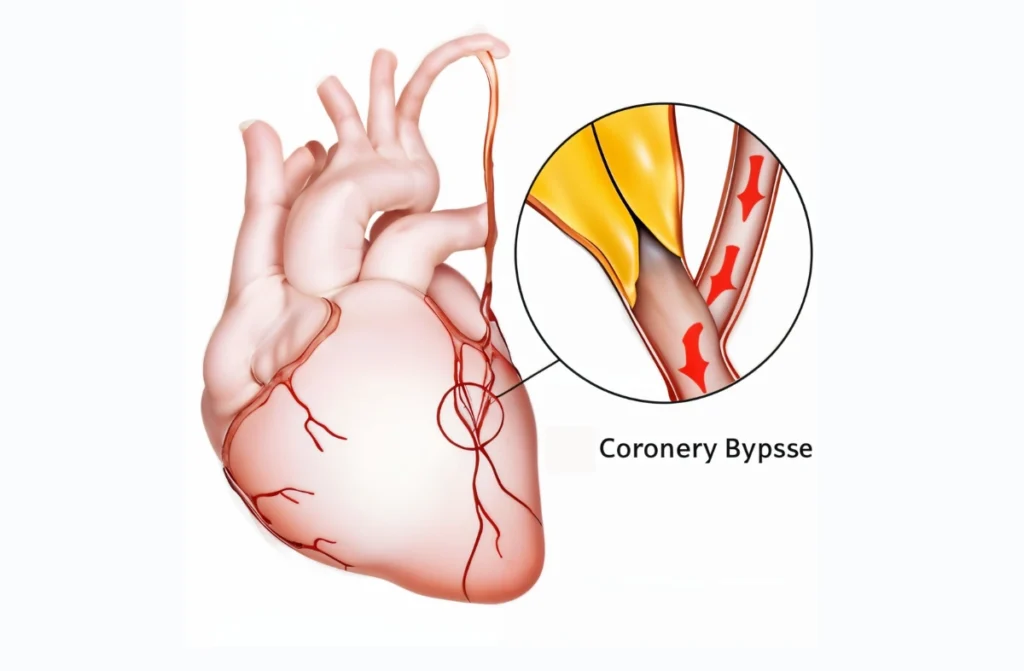
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): CABG is an open-heart surgery where a blood vessel, either from another part of the body or an artificial graft, is used to divert blood flow around the obstructed coronary artery, enabling it to bypass the blockage.
The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the extent and location of the Chronic Total Occlusions in Chennai, overall health condition, and individual circumstances.
Benefits and Risks
Chronic Total Occlusions carry both benefits and risks that need to be considered when determining the appropriate course of action for treatment.
Benefits
Treating chronic total occlusions (CTOs) can lead to improved blood flow, alleviating symptoms, and enhancing overall CTO cardiac intervention. It may prevent complications, such as heart attacks, and improve long-term cardiovascular health. Additionally, increased exercise tolerance and an improved quality of life are potential benefits.
Risks
Treatment of Chronic Total Occlusions in Chennai carries procedural risks, including bleeding, infection, and adverse reactions to anesthesia or medications. Restenosis, the recurrence of blockage, is a possible complication. Individual factors, such as overall health and complexity of the occlusion, also influence the risks. Weighing the benefits against the potential risks helps inform treatment decisions for CTOs.
Conclusion
To conclude, treating Chronic Total Occlusions in Chennai improves blood flow, relieves symptoms, and enhances patient outcomes. Advances in interventional techniques, such as retrograde approaches and dedicated CTO devices, have increased procedural success rates. Timely identification and appropriate management of CTOs are vital for optimizing patient care and reducing the risk of complications.