Percutaneous Valve Therapy in Chennai is a cutting-edge, minimally invasive treatment option for patients with heart valve diseases. This advanced procedure involves repairing or replacing heart valves through a catheter, eliminating the need for open-heart surgery. Chennai, renowned for its world-class healthcare facilities and expert cardiologists, is at the forefront of offering these innovative treatments.
Understanding Percutaneous Valve Therapy
What is Percutaneous Valve Therapy ?
Percutaneous valve therapy in Chennai is a minimally invasive procedure used to repair or replace heart valves without open-heart surgery. Techniques include:
1.Balloon Valvuloplasty: A balloon-tipped catheter inflates to widen a narrowed valve.
2.Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR): Replaces a stenotic aortic valve via catheter.
3.MitraClip: Clips together the leaflets of the mitral valve to reduce regurgitation.
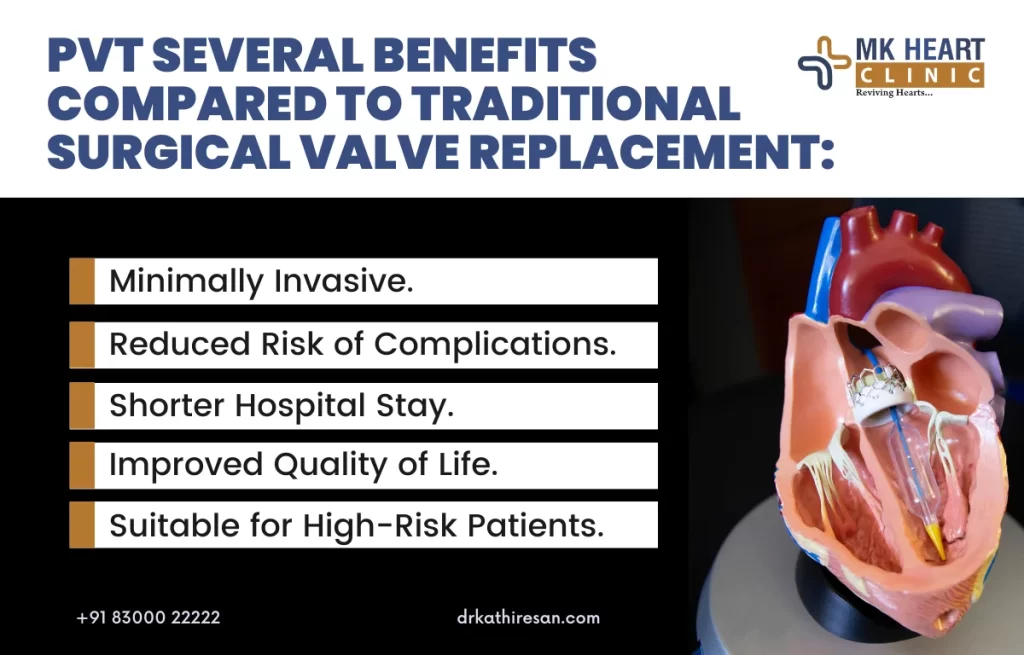
Benefits include shorter recovery time, reduced risk, and suitability for high-risk surgical patients. It’s commonly used for aortic and mitral valve conditions, improving symptoms and heart function significantly.
Types of Heart Valve Issues Treated
Percutaneous Valve Therapy is used to treat various heart valve conditions, including:
- Aortic Valve Stenosis: Narrowing of the aortic valve.
- Mitral Valve Regurgitation: Leakage of blood backward through the mitral valve.
- Pulmonary Valve Stenosis: Narrowing of the pulmonary valve.
- Tricuspid Valve Regurgitation: Leakage of blood backward through the tricuspid valve.
Each of these conditions can significantly impair heart function and overall health, making timely and effective treatment crucial.
Types of Percutaneous Valve Therapies
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) is a minimally invasive procedure used to replace a narrowed aortic valve that fails to open properly. During TAVR, a replacement valve is delivered to the heart through a catheter inserted into a blood vessel. This procedure is particularly beneficial for patients with severe aortic stenosis who are considered high-risk for traditional surgery.
Advancements in Imaging Techniques for Percutaneous Valve Therapy
Recent developments in imaging technologies have significantly enhanced the precision and safety of percutaneous valve therapies. Techniques such as real-time 3D echocardiography, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) angiography provide detailed anatomical information, allowing for accurate assessment and planning of interventions. These imaging modalities enable clinicians to visualize valve structures and surrounding tissues with high resolution, facilitating precise catheter navigation and optimal device placement. The integration of advanced imaging into percutaneous procedures has led to improved patient outcomes, reduced procedural risks, and expanded the applicability of minimally invasive valve treatments.
Procedure of TAVR
- Preparation: Patients undergo a series of diagnostic tests, including echocardiograms and CT scans, to determine the severity of the aortic stenosis.
- Catheter Insertion: A catheter is inserted through a small incision in the groin or chest and guided to the heart.
- Valve Deployment: The new valve is positioned within the damaged aortic valve and expanded, pushing the old valve leaflets out of the way.
- Completion: The catheter is removed, and the new valve immediately starts functioning.
TAVR has transformed the treatment landscape for aortic stenosis, offering a less invasive alternative with excellent outcomes.
Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement (TMVR)
Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement (TMVR) is a procedure used to replace the mitral valve in patients with severe mitral regurgitation. This minimally invasive approach is ideal for patients who cannot undergo open-heart surgery due to high surgical risks.
Procedure of TMVR
- Evaluation: Comprehensive evaluation through echocardiograms and other imaging techniques.
- Accessing the Heart: A catheter is inserted through a vein in the leg and guided to the heart.
- Valve Replacement: The new valve is deployed within the diseased mitral valve, ensuring proper function.
- Recovery: The catheter is removed, and the patient is monitored closely during recovery.
TMVR provides a safe and effective treatment option for patients with mitral valve disease, improving their quality of life and heart function.
Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Replacement (TPVR)
Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Replacement (TPVR) is used to replace the pulmonary valve in patients with congenital heart defects or pulmonary valve diseases. This procedure is particularly beneficial for pediatric patients and adults with repaired congenital heart defects.
Procedure of TPVR
- Diagnostic Tests: Detailed imaging and diagnostic tests to assess the pulmonary valve condition.
- Catheter Insertion: A catheter is inserted through a vein in the leg and navigated to the pulmonary valve.
- Valve Deployment: The new valve is positioned and expanded, replacing the diseased valve.
- Post-Procedure Care: Monitoring and follow-up care to ensure proper valve function and recovery.
TPVR offers a minimally invasive solution for pulmonary valve disease, reducing the need for repeat open-heart surgeries in patients with congenital heart defects.
Transcatheter Tricuspid Valve Replacement (TTVR)
Transcatheter Tricuspid Valve Replacement (TTVR) is an emerging procedure used to treat tricuspid valve regurgitation, a condition where the tricuspid valve does not close properly, leading to backward blood flow.
Procedure of TTVR
- Patient Assessment: Thorough assessment using echocardiograms and other imaging techniques.
- Access and Delivery: A catheter is inserted through a vein in the leg and guided to the tricuspid valve.
- Valve Placement: The new valve is deployed within the existing tricuspid valve, restoring proper valve function.
- Recovery and Monitoring: The catheter is removed, and the patient is monitored during recovery.
TTVR provides a promising treatment option for patients with severe tricuspid regurgitation, improving their heart function and symptoms.
Conditions Treated in Percutaneous Valve Therapy in Chennai
- Aortic Stenosis:
- Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR): Replaces the narrowed aortic valve to improve blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body.
- Mitral Regurgitation:
- MitraClip: Clips the mitral valve leaflets together to reduce backward blood flow.
- Mitral Stenosis:
- Balloon Valvuloplasty: Inflates a balloon to widen the narrowed mitral valve opening.
- Pulmonary Stenosis:
- Balloon Valvuloplasty: Widens the pulmonary valve to enhance blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs.
- Tricuspid Regurgitation:
- Percutaneous Tricuspid Valve Repair: Uses devices to improve valve function and reduce regurgitation.
- Congenital Heart Defects:
- Percutaneous Valvuloplasty or Valve Replacement: Corrects valve abnormalities present from birth.
These therapies provide effective treatment options, particularly for patients who are high-risk for traditional surgery.
Symptoms of Heart Valve Disease
There are not many symptoms for mild to moderate heart valve disease. But some of the most common symptoms which would require a heart patient to undergo percutaneous valve therapy in Chennai include:
1. Palpitations
2. Chest pain
3. Fatigue
4. Shortness of breath
5. Dizziness
6. Low or high blood pressure
7. Abdominal pain
8. Swelling in the legs
9. Whooshing sound
10. Irregular heartbeat
If you experience any of the above mentioned symptoms, it is always important to check with a doctor for a diagnosis for a safer side in order to avoid risky complications in the future.
Why Percutaneous Valve Procedures are Performed?
1. Minimally Invasive: Reduces recovery time and hospital stays compared to open-heart surgery.
2. High-Risk Patients: Suitable for patients who cannot undergo traditional surgery due to age or comorbidities.
3. Symptom Relief: Alleviates symptoms like shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue caused by valve disease.
4. Improved Quality of Life: Enhances daily functioning and overall well-being.
5. Reduced Complications: Lowers the risk of surgical complications, such as infections and excessive bleeding.
6. Immediate Benefits: Quickly restores proper blood flow and heart function.
7. Long-Term Outcomes: Offers durable results with significant improvements in heart health.
Percutaneous Valve Therapy – Options, Risks, and Benefits
Percutaneous Valve Therapy – Options
Percutaneous valve therapy encompasses several advanced treatment options designed to address various heart valve conditions using minimally invasive techniques. Here are the key treatment options available:
- Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR):
- Description: TAVR replaces a narrowed aortic valve without the need for open-heart surgery. A catheter is inserted through a blood vessel, usually in the groin or chest, and guided to the heart where a new valve is expanded into place.
- Indications: Severe aortic stenosis in patients considered high-risk for traditional surgical valve replacement.
- Benefits: Reduced recovery time, lower risk of complications like infection, and improved quality of life post-procedure.
- Transcatheter Mitral Valve Replacement :
- Description: MitraClip is used to treat mitral regurgitation by clipping together the leaflets of the mitral valve to reduce backward blood flow without replacing the valve.
- Indications: Chronic mitral regurgitation in patients who are not candidates for surgery.
- Benefits: Improves symptoms such as shortness of breath and fatigue, with minimal recovery time compared to surgical options.
- Balloon Valvuloplasty:
- Description: This procedure involves inserting a balloon-tipped catheter into a narrowed heart valve (such as mitral or pulmonary) and inflating it to widen the valve opening.
- Indications: Symptomatic stenosis (narrowing) of heart valves, especially in cases where valve replacement is not immediately indicated.
- Benefits: Provides temporary relief by improving blood flow and reducing symptoms, although it may not be a permanent solution for all cases.
- Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Replacement (TPVR):
- Description: TPVR is used to replace a dysfunctional pulmonary valve through catheter-based techniques, typically for congenital heart defects or previous surgical interventions.
- Indications: Pulmonary valve dysfunction, often seen in patients with congenital risk for heart diseases like Tetralogy of Fallot.
- Benefits: Minimally invasive approach reduces surgical risks and recovery time, offering effective long-term valve function.
- Transcatheter Tricuspid Valve Replacement :
- Description: Various devices and techniques are employed to improve tricuspid valve function and reduce regurgitation, often through annuloplasty or edge-to-edge repair.
- Indications: Tricuspid regurgitation secondary to conditions such as mitral valve disease or right heart failure.
- Benefits: Helps restore valve function and improve symptoms, especially in patients with prohibitive surgical risks.
These Percutaneous Valve Therapy in Chennai represent significant advancements in cardiovascular medicine, offering tailored approaches to treating valve diseases with reduced invasiveness and improved patient outcomes compared to traditional open-heart surgeries. Each option is selected based on individual patient characteristics, valve pathology, and overall health considerations to achieve optimal results and enhance quality of life.
Percutaneous Valve Therapy – Risks
- Vascular Complications:
- Bleeding or damage to blood vessels during catheter insertion.
- Valve-related Complications:
- Risk of valve leakage, embolism, or device malfunction.
- Infection:
- Potential infection at catheter insertion site.
Percutaneous Valve Therapy – Benefits
- Minimally Invasive:
- Shorter recovery and hospital stay compared to open-heart surgery.
- Improved Symptoms:
- Relieves symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
- Suitability for High-Risk Patients:
- Options for patients unable to undergo traditional surgery due to risks.
- Enhanced Quality of Life:
- Improves daily functioning and overall well-being post-procedure.
Why Choose Dr. Kadhiresan for Percutaneous Valve Therapy in Chennai
Dr. Kadhiresan is renowned for his expertise and experience in performing Percutaneous Valve Therapy in Chennai. Here’s why he stands out as a top choice:
- Extensive Experience: With years of experience, Dr. Kadhiresan has successfully treated numerous patients with heart valve issues, providing advanced care tailored to each individual’s needs.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: Dr. Kadhiresan uses the latest technology and techniques in Percutaneous Valve Therapy in Chennai, ensuring precision and improved outcomes for his patients.
- Patient-Centered Care: He focuses on providing personalized treatment plans, ensuring that patients are well-informed and comfortable throughout the process.
- High Success Rate: His expertise has led to a high success rate in performing minimally invasive valve treatments, enhancing patients’ recovery and quality of life.
- Comprehensive Follow-Up Care: Dr. Kadhiresan ensures that every patient receives thorough follow-up care to monitor their progress and address any concerns.
Choosing Dr. Kadhiresan guarantees access to expert care for those seeking Percutaneous Valve Therapy in Chennai.
Conclusion
If you or anyone who is in need of percutaneous valve therapy in Chennai, you can approach MK Heart Clinic as this best heart clinic in Chennai has a highly experienced team of cardiovascular surgeons and interventional cardiologists who are specialized in Performing these minimally invasive procedures with the most extensive catheterization facilities ensures high precision, safety, and optimal patient outcomes. Advanced imaging technology, state-of-the-art equipment, and a skilled medical team enable accurate diagnosis and effective treatment with minimal discomfort. These facilities are designed to support complex cardiac interventions, reducing procedure time, hospital stays, and recovery periods.
Read also: Best Foods for A Healthy Heart.

