Heart Rate in Hypertension, often referred to as high blood pressure, is a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This condition can stealthily infiltrate our lives, often going unnoticed, but it carries significant health risks. Amid the myriad factors contributing to hypertension, heart rate emerges as a crucial element that warrants our focus.
In this blog article, we will investigate the connection between heart rate and hypertension, delving into the importance of heart rate in comprehending and effectively managing this condition.
Heart Rate in Hypertension: The Crucial Connection
In people with hypertension, their heart rate, which measures the number of heartbeats per minute, often falls outside the typical range of 60 to 100 beats per minute. This variation in heart rate is associated with the body’s effort to maintain balance when blood pressure increases.
The heart accelerates its pumping rate to ensure an adequate supply of oxygen-rich blood to vital organs, assisting the body in dealing with heightened pressure. Although this increased heart rate is a valuable short-term response, comprehending this fluctuation is crucial for the effective management of hypertension.
One of the key connections between heart rate and hypertension lies in the body’s attempt to maintain an equilibrium. When blood pressure rises, your heart rate may increase as a compensatory mechanism.
The heart pumps faster to deliver more oxygen-rich blood to various organs and tissues, helping to cope with the elevated pressure. This is your body’s way of responding to increased demand and, in the short term, can be a helpful mechanism.
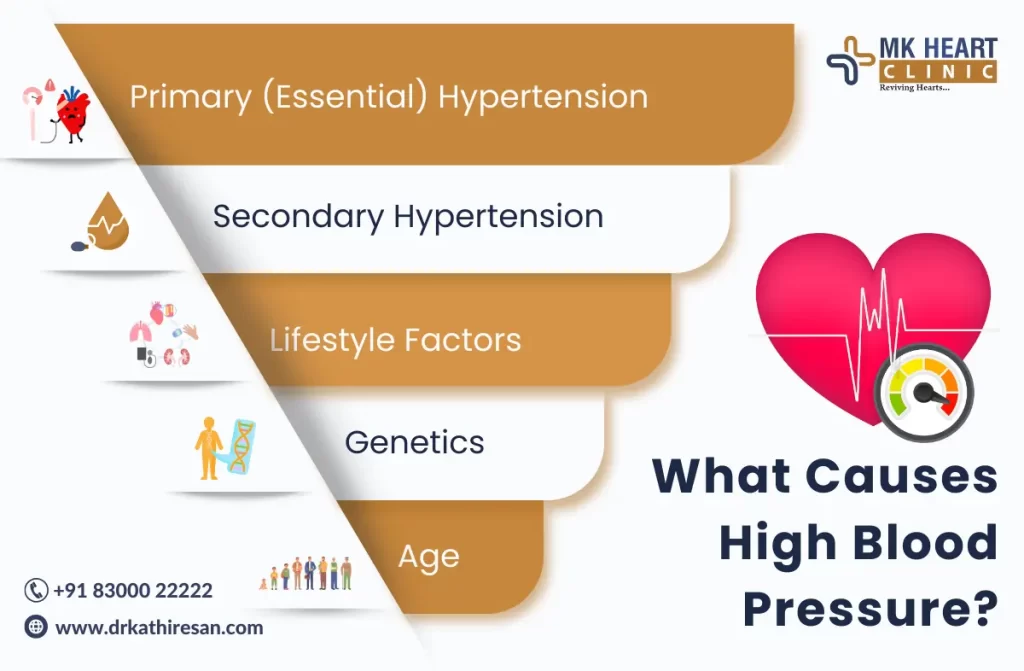
Heart Rate in Hypertensive Heart Failure: A Complex Relationship
Heart Failure, a severe condition resulting from uncontrolled hypertension, causes the heart to struggle in pumping blood efficiently. The heart may beat faster in heart failure, attempting to compensate for its reduced pumping efficiency. However, this can worsen the condition by increasing the heart’s workload. Hence, comprehending and managing heart rate is crucial to prevent heart failure.
In heart failure, the heart may beat faster as it tries to compensate for its reduced pumping efficiency. This can be detrimental because it increases the heart’s workload, potentially worsening the condition. Therefore, understanding and managing heart rate is crucial for individuals with hypertension to prevent the development of heart failure.
Medications and Heart Rate in Hypertension
Medications are commonly prescribed for hypertension management, and some, like beta-blockers, directly affect heart rate. Beta-blockers work by slowing down the heart rate and blocking the effects of adrenaline, effectively lowering blood pressure, and proving effective in managing hypertension.
Lifestyle Modifications for Controlling Heart Rate Hypertension
In addition to medications, lifestyle changes are essential for heart rate and blood pressure control in individuals with hypertension, emphasizing the keyword Heart Rate in Hypertension. Incorporate the following changes:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity enhances heart health, reducing the need for the heart to beat faster to maintain blood flow. Aim for 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly.
- Diet: opt for a heart-healthy diet low in sodium, and rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to control blood pressure and heart rate. Reducing salt intake is especially important.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress elevates heart rate and blood pressure. Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga to manage stress and keep heart rate in check.
- Weight Management: Maintaining an optimal weight is essential for cardiovascular well-being. Excess weight strains the heart, increasing heart rate and blood pressure. Adopt a balanced diet and regular exercise to achieve and sustain a healthy weight while managing Heart Rate in Hypertension.
Conclusion
In the intricate world of heart rate in hypertension, heart rate plays a pivotal role. While an elevated heart rate may initially serve as a compensatory mechanism to cope with increased blood pressure, it can lead to detrimental consequences in the long run, including hypertensive heart failure. Understanding the relationship between heart rate and hypertension is vital in managing this condition effectively.
Also Read Best Interventional Cardiologist In Chennai.