Living with a leaky heart valve doesn’t mean giving up on physical activity. In fact, choosing the best exercise for a leaky heart valve can be one of the smartest steps in heart valve disease prevention. With the right movements and guidance, you can boost cardiovascular strength, support valve function, and improve your quality of life.
What Is a Leaky Heart Valve?
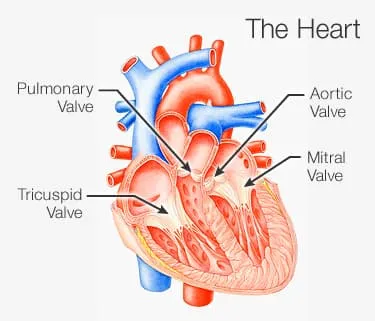
A leaky heart valve, also known as valvular regurgitation, occurs when one or more heart valves do not close properly, allowing blood to flow backward instead of moving forward efficiently. This can lead to symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, and heart palpitations. Over time, the condition may weaken the heart, making it essential to follow medical advice, including lifestyle changes and the best exercise for leaky heart valve to support cardiovascular function.
How Is a Leaky Heart Valve Diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose a leaky heart valve using various tests, including
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test provides images of the heart to assess valve function.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Measures the heart’s electrical activity to detect irregularities.
- Cardiac MRI: Produces detailed heart images to evaluate the severity of valve leakage.
- Stress Test: Monitors heart performance during exercise to determine the impact of a leaky heart valve.
Once diagnosed, a personalized plan is created, including recommendations for the best exercise for leaky heart valve to keep the heart strong without causing strain.
Safety Considerations Before Starting Any Exercise
Before engaging in any fitness program for a heart condition, it’s crucial to consider the following
- Consult your cardiologist. Always get clearance before beginning new physical activity.
- Understand your condition: The severity of the leaky valve affects the type and intensity of exercise.
- Start slow: Low-impact workouts are safest, especially during the early stages.
- Listen to your body. Fatigue, shortness of breath, or chest pain are red flags.
- Monitor heart rate: Using a wearable monitor helps avoid overexertion.
These precautions will ensure you’re choosing the best exercise for a leaky heart valve tailored to your health status and limitations.
Best Exercises for a Leaky Heart Valve

Physical activity is essential, but choosing the right exercise matters. The best exercise for a leaky heart valve includes
- Walking: A low-impact workout that keeps the heart active without excessive strain.
- Swimming: Enhances cardiovascular endurance while reducing stress on joints and heart.
- Cycling: Engages the cardiovascular system with controlled effort levels.
- Yoga: Promotes relaxation, improves circulation, and strengthens the heart over time.
- Light Resistance Training: Helps maintain muscle strength while improving overall heart function.
Always consult a doctor before starting any new exercise regimen. The best exercise for a leaky heart valve should match individual fitness levels and medical conditions.
Symptoms of a Leaky Heart Valve
The severity of symptoms varies, but common signs include
- Shortness of breath: Especially during physical activity or when lying flat.
- Fatigue: A feeling of exhaustion due to inefficient blood circulation.
- Heart palpitations: A fluttering sensation caused by irregular heart rhythms.
- Swollen ankles or feet: Fluid retention can occur due to poor circulation.
- Dizziness or fainting: In severe cases, inadequate blood flow can affect brain function.
Recognizing these symptoms early can help in adopting heart-friendly activities, including the best exercise for leaky heart valve to enhance overall health.
Leaky Heart Valve and Aortic Regurgitation
Aortic regurgitation is a specific type of leaky heart valve affecting the aortic valve. This condition causes blood to flow back into the left ventricle, making the heart work harder to pump blood efficiently. If left untreated, it can lead to heart failure.
People with aortic regurgitation should follow a carefully designed fitness plan, including:
- Moderate Aerobic Exercises: Walking, swimming, and stationary cycling.
- Strength Training with Caution: Avoid heavy lifting; use light weights and controlled movements.
- Mindful Breathing Practices: Yoga and meditation can reduce heart strain.
The best exercise for leaky heart valve, including aortic regurgitation, should focus on maintaining heart function without causing unnecessary exertion.
How to Strengthen Heart Valves Naturally
A strong heart supports better valve function. Here are key ways to improve heart valve health:
- Balanced Diet: Include omega-3-rich foods like salmon, nuts, and seeds.
- Regular Exercise: Walking, cycling, and stretching exercises improve circulation.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water prevents dehydration, which can strain the heart.
- Stress Management: Meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help reduce cardiovascular stress.
- Adequate Sleep: Proper rest allows the heart to recover and function optimally.
Following these steps, along with the best exercise for heart, can contribute to overall cardiovascular well-being.
What Are Suitable Exercises for Those with a Leaky Heart Valve?
For individuals with a leaky heart valve, suitable exercises include
- Walking: One of the safest and most effective exercises for cardiovascular health.
- Tai Chi: A gentle movement-based exercise that improves circulation and relaxation.
- Elliptical Training: A low-impact alternative to running, reducing joint and heart strain.
- Stretching and Flexibility Workouts: These improve mobility and reduce tension on the body.
Each person’s tolerance varies, so it is vital to consult a healthcare provider to determine the best exercise for leaky heart valve that suits individual health conditions.
Is Walking a Cardio Workout
Walking is one of the simplest and most accessible forms of exercise. But is walking a cardio workout? Many people assume that cardio means high-intensity activities like running or cycling, but walking can be just as effective for improving heart health. At MK Heart Clinic, we believe that walking is a great way to keep your cardiovascular system strong, improve endurance, and enhance overall well-being. In this blog, we’ll explore the benefits of walking, how it compares to other cardio workouts, and the best ways to maximize its effects.
Is Walking Good for a Leaky Heart Valve?
Many wonder, is walking good for leaky heart valve? The answer is a definite yes! Walking is one of the best exercises for maintaining cardiovascular health while ensuring minimal strain on the heart. Benefits of walking include:
- Improved Circulation: Walking promotes blood flow and oxygen supply to the heart.
- Lowered Blood Pressure: A consistent walking routine helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
- Stress Reduction: It aids in relaxation, reducing stress-related heart strain.
- Better Weight Management: Walking helps control weight, reducing unnecessary pressure on the heart.
Incorporating daily walks as part of the best exercise for leaky heart valve plan can significantly improve heart function and overall well-being.
Heart Valve Disease Prevention
Heart valve disease prevention involves:
- Exercise: Engaging in heart-friendly workouts like walking and swimming.
- Healthy Eating: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Stress Reduction: Lowering stress through meditation and mindfulness.
- Routine Medical Visits: Keeping track of heart health through regular check-ups.
- Avoiding Infections: Maintaining dental hygiene to prevent infections that can affect heart valves.
By adopting these habits, heart valve disease prevention becomes manageable, ensuring a healthier heart.
Benefits of Exercise for Heart Valve Health
Regular physical activity isn’t just about fitness—it actively supports heart function. The best exercise for a leaky heart valve promotes
- Improved blood flow and oxygenation
- Lower blood pressure
- Weight management
- Better stress response
- Stronger heart muscles and valves
This aligns perfectly with the goal of heart valve disease prevention and encourages a healthier lifestyle.
Why Exercise Is Important After Stent Placement
- Strengthens Heart Muscles: Gradually improves heart efficiency.
- Promotes Better Blood Flow: Helps prevent future blockages.
- Reduces Risk Factors: Controls blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Boosts Mental Health: Reduces anxiety and depression after a heart attack.
Patients treated at the best exercise after heart attack stents are guided through customized cardiac rehabilitation programs. Their rehabilitation experts emphasize beginning slowly and increasing intensity over time. Consulting the best expert for stent placement in Chennai ensures your exercise regimen suits your health condition.
Quick Tips for Safe Exercise Routine
When designing your routine around the best exercise for a leaky heart valve, keep these tips in mind:
- 🧘 Warm-up and cool down with stretches
- ⏱️ Keep sessions short but consistent
- 💧 Stay hydrated
- 📋 Log your progress and symptoms
- 🧠 Maintain a positive mindset
These steps go hand-in-hand with how to strengthen heart valves and ensure long-term heart health.
Conclusion
Best exercise for a leaky heart valve is essential for maintaining heart health and overall fitness. Safe and effective workouts like walking, swimming, and light resistance training play a crucial role in managing this condition. The MK Heart Clinic emphasizes the importance of tailored exercise plans for individuals with heart valve issues. Heart valve disease prevention, combined with lifestyle modifications, helps in sustaining long-term heart health. For personalized advice and expert guidance, contact the MK Heart Clinic today and take the first step towards a healthier heart.
Read also: Snoring and Heart Disease

